

Microscopic modeling of the relaxation phenomenon using a macroscopic lane-changing model. Forthcoming in Proceedings of The Royal Society A, 2010. Mechanism to describe stop-and-go waves: A mechanism to describe the formation and propagation of stop-and-go waves in congested freeway traffic. (2003) Dynamic travel time prediction with real-time and historic data, Journal of Transportation Engineering, Vol. (2002) Performance evaluation of short-term time-series traffic prediction model, Journal of Transportation Engineering, Vol. (2002) Travel Time Prediction by Advanced Neural Network., Periodica Polytechnica Civil Engineering, Vol. Proceedings of 6th World Congress on Intelligent Transport Systems, Toronto, Canada. (1999) Dynamic Travel Time Estimation on Instrumented Freeways. (1994) Artificial Intelligence Applications to Traffic Engineering. Because off-the-shelf commercial simulation packages do not perform well in saturated freeways, we will use a traffic simulation model being developed at Georgia Tech, which is able to predict realistic traffic dynamics on congested freeways. This would allow us to predict the onset and propagation of congestion trough the network, and to improve current "real-time" travel time estimates in NaviGAtor (which are usually displayed with a ~10 min delay). This project will incorporate recent advances in traffic flow theory and simulation to build a framework able to provide short-term (up to ~30 min) travel time forecasts across the metropolitan Atlanta freeway network. The model proposed in this project overcomes these drawbacks by incorporating the latest advances in traffic flow theory and simulation.
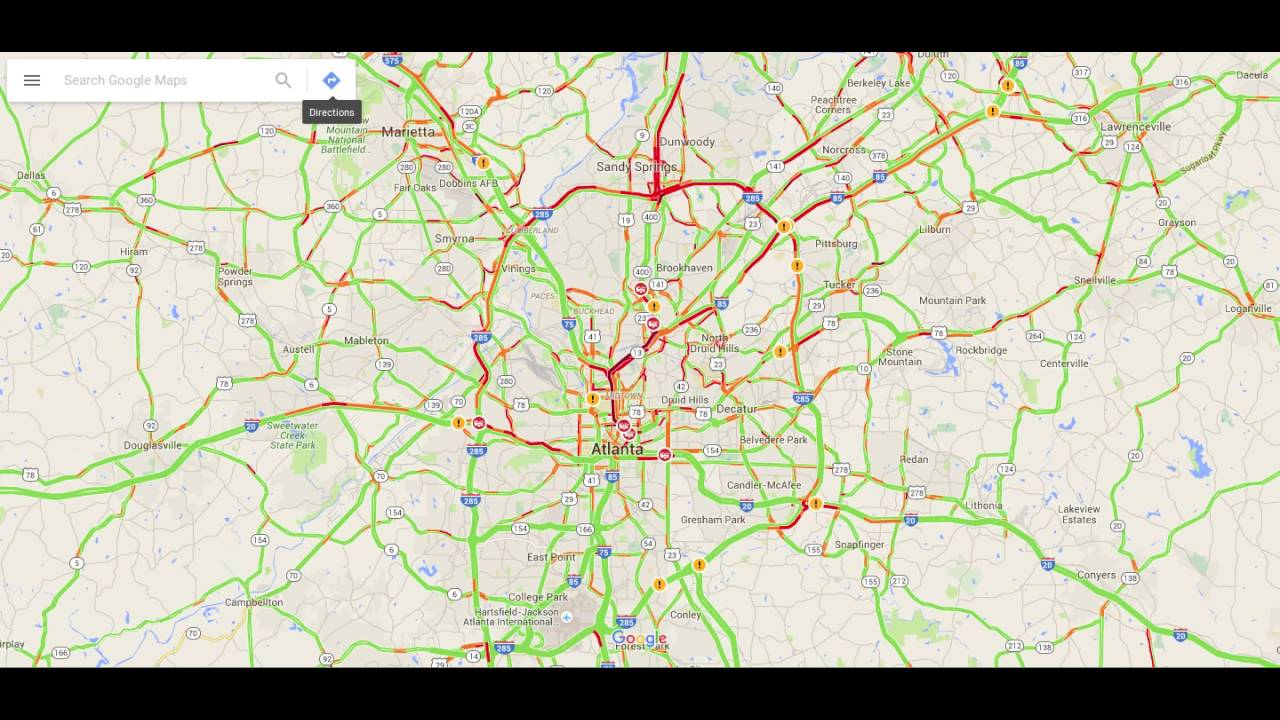
Although successful, the German example is based on a type of simulation model (a Cellular Automata model) that has important drawbacks: difficult to calibrate, unable to incorporate different user classes (e.g., cars and trucks), and not proven to replicate detailed traffic dynamics on freeways. Simulation-based forecast system is already in place at most metropolitan areas, with very favorable user impacts. Unfortunately, this approach is unable to produce reliable forecasts because it does not take into account traffic dynamics (e.g., via a simulation model). The vast majority of real-time travel time estimation algorithms proposed in the literature are based on data mining techniques. outages due to detector or cameras malfunction. Additionally, spatial forecast can help GDOT provide reliable information in areas with temporary outages in coverage e.g. Forecasts built into the estimation model will make the travel-time estimates more accurate by reducing the use of stale data. In this context, the ability to forecast traffic conditions (both in space and time) would augment the services provided by NaviGAtor by allowing users to plan ahead for their trip. and the advancement of the 511 traffic information system will require the Traffic Management Center to provide more detailed and accurate traffic information to an increasing number of users. The increasing number of Variable Message Signs, addition of services such as My-NaviGAtor, NaviGAtor-to-go etc. Real-time traffic information provided by GDOT has proven invaluable for commuters in the Georgia freeway network. Jorge Laval, Assistant Professor, Georgia Tech Angshuman Guin, Senior Research Engineer, Georgia Techĭr.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
